-
Statistics:
-
Control of false discovery rates in multiple testing and asymmetric errors in binary classification
-
Measures of association
-
High-dimensional linear model inference and variable selection
-
Bipartite network stochastic block model inference
-
-
Bioinformatics / Statistical Genomics:
-
Statistical rigor in omics data analysis
-
Statistical method development for single-cell omics data
-
Statistical method development for bulk short-read RNA-seq data
-
Using statistics to quantitate the Central Dogma, the fundamental principle of molecular biology
-
Comparative genomics: developing novel statistical methods to investigate conserved or divergent biological phenomena in different tissue and cell types across multiple species
-
Identification of gene-gene and protein-DNA interactions using diverse genomic data
-
Featured Research
The advancement of next-generation high-throughput sequencing technologies has been revolutionizing genomic studies in the last decade. In particular, the RNA sequencing (RNA-seq) technology, which has deep coverage and base level resolution, enables investigating human and other eukaryotic species’ transcriptomes (i.e., sets of RNA molecules in cells) with unprecedented detail and clarity. Unlike previous technologies such as microarrays, RNA-seq provides information on alternative splicing (i.e., how is the DNA of one gene possibly transcribed...
We have investigated how to use statistics to quantitate the Central Dogma: DNA makes mRNA, and mRNA makes protein, one of the most fundamental principles in modern biological sciences. There are two key synthesis steps: transcription (information flow from DNA to mRNA) and translation (information flow from mRNA to protein). In addition, mRNA and protein molecules are degraded (i.e., destroyed), making four steps in total. In the past seven years, I collaborated with Dr. Mark Biggin, a biochemist at Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory,...
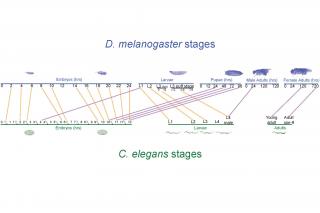
We have developed two new statistical metrics “TROM” (TRanscriptome Overlap Measure) and “EPOM” (EPigenome Overlap Measure) to evaluate the similarity of transcriptomes andepigenomes (i.e., sets of chemical compounds that are not part of the DNA sequence but are on or attached to DNA) within and across species. In work with the modENCODE consortium [1, 2, and 3], we used TROM to discover a previously unknown conservation between the developmental stages of D. melanogaster and C. elegans, two vastly different model organisms...
We have worked on statistical methodology development in the following projects, which were motivated by prominent biomedical research questions. The methods we developed have great potential to become critical tools in computational biology and medical informatics.
First, we have developed a “new R²” association measure for describing complex gene interactions. Capturing important gene expression relationships is a key component in computational biology research (e.g. network study). Commonly used measures such as Pearson correlation and Spearman rank...